Contents:
Common Names | Parts Usually Used | Plant(s) & Culture | Where Found | Medicinal Properties | Biochemical Information
Legends, Myths and Stories | Uses | Formulas or Dosages | Nutrient Content | How Sold | Warning | Resource Links
Scientific Names

- Argania spinosa
- Argania sideroxylon
- Sideroxylon argan
- Sideroxylon spinosum L.
- Sapotaceae family
Common Names
- Argan Oil
- Argan Tree
- Morocco Ironwood
- Spiny Argania
Parts Usually Used
The entire plant, especially the fruits
Back to Top
Description of Plant(s) and Culture
Argan trees typically grow to a height of 8-10 meters and can live up to 200 years.The tree has many thorns and the trunk is usually gnarled, the branches lean toward the ground. Its leaves measure only about 2-4 cm in lengthand are oval in shape. The tree flowers in April, boasting small pale yellow petals. The fruits measure about 2-4 cm in length and have a thick, bitter peel around the sweet-smelling pulp. Inside the pulp is a very hard nut that contains oil-rich seeds. The nuts only mature once each year, usually in June or July.
Back to Top
Where Found
Argan trees are found growing in Morocco, Algeria, Western Sahara, Mauritania, Australia, Canary Islands, East Africa, Egypt, Haiti, Israel, Kenya, Libya, Mediterranean, Spain and Sudan.
Back to Top
Medicinal Properties
The argan tree and its oil are known to have antioxidant, antimalarial, anti-inflammatory, cardio-protective, Lipid lowering, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, cytoprotective and antibacterial properties.
Studies have shown that argan oil helps prevent prothrombotic complications in patients and it modulates insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in animals.
Research has reported that consuming argan oil for only 5-8 weeks caused an improvement in metabolic syndrome, as well as lessening of pain and walking difficulties in rheumatology and arthritis patients. It also helps prevent or lessens neurodegenerative diseases, inflammation and other age-related health issues.
Additional studies have seen promising results for antibacterial effects against antibiotic-resistant infections such as MRSA and MSSA.
Argan oil has been shown to contain antioxidants; plays a role in prevention of cardiovascular disease; reduces of LDL cholesterol; is said to cure pimples, acne, and chicken poxpustules; treats skin wrinkles and dryness; is a common treatment for rheumatologic problems; aids in joint movement with arthritis; is a hepatoprotective agent; offers atherosclerosis reduction; reduces plasma cholesterol; treatment for arterial hypertension and insulin resistance; increases the efficiency of prostaglandins; is said to reduce the aging process; controls prostate cancer; promotes softness and protection of hair; offers antiatherogenic activity; is said to offer some protections against skin cancer; has antidiabetic and antimalarial properties; and immune system enhancing properties.
Back to Top
Biochemical Information
Argan oil contains myristic acid, palmitic acid, palmitoleic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, linolenic acid, arachidonic acid, gadoleic acid and behenic acid. The oil is rich in essential fatty acids, contains 80% unsaturated fatty acids and is more resistant to oxidation than olive oil. It also contains carotenoids, sterols, polyphenols, tocopherols, saponins, xanthophyls and antioxidants.
Argan oil is also rich in Long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFA). These are known to promote brain functions, and protect brain plasticity and memory processes.
Back to Top
Legends, Myths and Stories
 The argan tree is often seen full of climbing goats! They climb it to eat the fruits. The fruits that are spat out by the goats are also gathered for use in making argan oil. However, the idea that goat poop is harvested to get the fruits is only a myth.
The argan tree is often seen full of climbing goats! They climb it to eat the fruits. The fruits that are spat out by the goats are also gathered for use in making argan oil. However, the idea that goat poop is harvested to get the fruits is only a myth.
The argan tree is now on the Red List of Threatened Plants.
The argan tree is often planted to prevent soil erosion due to its extensive root system.
Trees are often planted as wind breakers and are used for fencing.
Because argan wood is very heavy, hard and durable it is used a lot in carpentry.
Argan wood is valued for its use as fuel and charcoal.
Several women’s cooperatives produce argan oil, providing an important socioeconomic function in the areas where the tree grows. It is estimated that this production of argan oil currently supports about 2.2 million people in that region.
Manual production of argan oil begins by removing the soft pulp of the fruit for use in animal feed. Then, the hard nut is cracked by hand between two stones to remove the seeds. They are then roasted and ground to a paste with a little water. This paste is hand-squeezed to extract the oil. The remaining paste is used as animal feed, so there is little to no waste in the process.
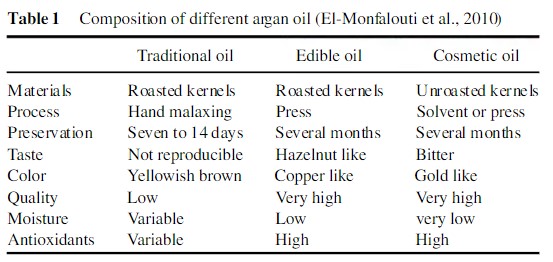
Uses
 Argan oil is used by the locals to dip bread, add to couscous or on salads, etc.
Argan oil is used by the locals to dip bread, add to couscous or on salads, etc.
Unroasted argan oil is used as a treatment for skin ailments and is often used as an additive for cosmetics.
Sheep, goats, camels and cattle all use argan trees as a forage source of food. The fruits and leaves are also fed to livestock.
The oil is used like olive oil for cooking, frying and salad dressings.
The paste that is leftover after oil extraction (a thick chocolate-colored paste called ‘amlou’) has a taste similar to peanut butter once it is sweetened.
Argan oil obtained from the seed is used for lighting and to make soap.
Argan oil is used on hair that has been color-treated to decrease the damage from the treatment.
Back to Top
Formulas or Dosages
Some local people create a dip for bread known as amlou by combining argan oil, almonds, and peanuts, sometimes it is sweetened by honey or sugar.
Back to Top
Nutrient Content
Rich source of Vitamin E
Back to Top
How Sold
Argan oil is sold in bulk for cooking and in smaller quantities for cosmetic use.
Back to Top
Warning
In rare cases, people have been known to experience anaphylaxis and toxicity to argan oil. If you start to experience shortness of breath, swelling of the lips or of the tongue, contact emergency medical help immediately!
Back to Top
Resource Links
Physicochemical Characteristics,Nutritional Properties, and HealthBenefits of Argan Oil: A Review
Therapeutic potential of argan oil: a reviewjphp_1190 1669..1675
Antidiabetic Activity Assessment of Argania spinosa Oil
Protective effect of saponins from Argania spinosa against free radical-induced oxidative haemolysis
