Contents:
Common Names | Parts Usually Used | Plant(s) & Culture | Where Found | Medicinal Properties
Legends, Myths and Stories | Uses | Formulas or Dosages | Nutrient Content | How Sold | Resource Links | Bibliography
Scientific Names

- Phaseolus vulgaris L.
- Pea family
Common Names
- Common bean
- Dou fu-tofu (bean curd)
- Green bean
- Kidney bean
- Navy bean
- Pinto bean
- Snap bean
- String bean
- Wax bean
Parts Usually Used
Beans and pods
Back to Top
Description of Plant(s) and Culture
The Kidney bean is an annual, twining plant; the leaves are alternate, each leaf consisting of 3 broad-ovate to rhombic-ovate, entire, pointed leaflets. The white, yellow or purplish flowers grow in sparse, axillary clusters. The fruit is a green or yellow pod; the color of the seeds, or beans, depends on the variety. Diverse as they are, all the beans named above are varieties of the kidney bean. The dry beans are picked when mature, the others at various stages of maturity.
Back to Top
Where Found
Probably originated in South America and is still the predominant bean cultivated in the Americas.
Back to Top
Medicinal Properties
Diuretic
Back to Top
Legends, Myths and Stories
Phaseolus vulgaris (kidney bean) is indigenous to the Americas, being unknown to the rest of the world before Columbus. This species includes the common green bean as well as wax beans, and various dried beans such as red kidney, pinto, and navy. These beans were extensively cultivated and used as trade goods by Native American tribes from Canada to South America, with each tribe having its own names and folklore for the beans.
Before the discovery of the New World, Europeans did have other bean species with various traditions associated with them. On
Since 200 BC, tofu (bean curd) has been cooked into a soup to treat colds; the Chinese version of chicken soup. Tofu can be stored up to
It is claimed, if the green pods are chewed in ones mouth and applied to any place bitten by a horse, it will help.
Back to Top
Uses
Bean pods are effective in lowing blood sugar levels and can be used (with the concurrence of a doctor) for mild cases of diabetes. A bean pod diet for this purpose would mean eating
Back to Top
Formulas or Dosages
Use anywhere from
Back to Top
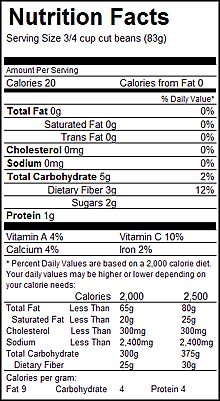
Nutrient Content
How Sold
Supermarket: fresh or dried
Back to Top
Resource Links
LiveStrong.com: Number of Calories Per Ounce of Pinto Beans
USDA Nutrition Database: Pinto Beans
Food.com: Kitchen Dictionary: Pinto Bean
Bibliography
![]() The Herbalist Almanac
The Herbalist Almanac, by Clarence Meyer, Meyerbooks, publisher, PO Box 427, Glenwood, Illinois 60425, copyright 1988, fifth printing, 1994
![]() Planetary Herbology
Planetary Herbology, by Michael Tierra, C.A., N.D., O.M.D., Lotus Press, PO Box 325, Twin Lakes. WI 53181., Copyright 1988, published 1992
 Earl Mindell’s Herb Bible
Earl Mindell’s Herb Bible, by Earl Mindell, R.Ph., Ph.D., Simon & Schuster/Fireside, Rockefeller Center 1230 Avenue of the Americas, New York, New York 10020
![]() Culpeper’s Complete Herbal & English Physician: Updated With 117 Modern Herbs
Culpeper’s Complete Herbal & English Physician: Updated With 117 Modern Herbs, by Nicholas Culpeper, Meyerbooks, publisher, PO Box 427, Glenwood, Illinois 60425, 1990, (reprint of 1814)
 Old Ways Rediscovered
Old Ways Rediscovered, by Clarence Meyer, Meyerbooks, publisher, PO Box 427, Glenwood, Illinois 60425, published from 1954, print 1988
 Prairie Smoke
Prairie Smoke, by Melvin R. Gilmore, Minnesota Historical Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota 55101, copyright 1987.
![]() The Herb Book
The Herb Book, by John Lust, Bantam Books, 666 Fifth Avenue, New York, NY. copyright 1974.
![]() Webster’s New World Dictionary
Webster’s New World Dictionary, Third College Edition, Victoria Neufeldt, Editor in Chief, New World Dictionaries: A Division of Simon & Schuster, Inc., 15 Columbus Circle, New York, NY 10023
